|
Tule
Ponds at Tyson
PHYTOPLANKTON |
 |
|
The organisms that live in pond water
are part of the invisible world that nourishes the
ecosystem. Plankton consists of two components:
phytoplankton and the zooplankton. Phytoplankton include
photosynthetic floaters in the water column. Since
phytoplankton require light they are usually found only
where light can penetrate. Usually light can penetrate
throughout the water column in a small pond, but this
depends on the turbidity of the ponds. Zooplankton
includes representatives from protist as well as many
invertebrates. Many invertebrates like arthropods and
mollusks have a larval stage which is spent as plankton.
Together these microorganisms are
important because they provide food for many of the larger
organisms of the pond. Zooplankton consume other
zooplankton and phytoplankton. Fish consume phytoplankton
and zooplankton. |
Microscopic algae or phytoplankton come
in a variety of shapes and in varied colors due to their
different photosynthetic pigments. Algae can be unicellular and
microscopic or colonial forming plate-like colonies, thread-like
filaments, net-like tubes, or hollow balls.
DIATOMS
Identified by Ray Wong |
|
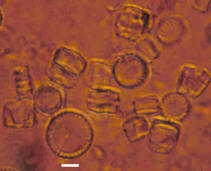 Cyclotella sp. Cyclotella sp.
Centric diatom. Planktonic (floater)
Family Coscinodiscaceae.
White scale bar is 5 microns
Cells usually
solitary, but sometimes united to short chains. Valves circular,
strongly to weakly undulate, undulations more evident in the middle
area. Middle area punctuate, marginal area striate. Valve disc
divided into two portions, the exterior annular, with striae smooth
(costae) or punctuate, more or less fine, sometimes intermixed with
small spines; always without a pseudo-nodule; center often bullate,
smooth or granular, with granules sparse or radiating. |
|
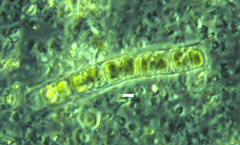 Melosira (Melosira sp.) Melosira (Melosira sp.)
Centric diatom. Planktonic (floater)
Family Coscinodiscaceae.
White scale bar is 5 microns
Cells closely
united to more straight; beadlike chains in the middle of the valve
faces. Frustules globose, elliptical or cylindrical. Valves
circular, often deeply convex and possessing a deep valve mantle,
often with "small teeth" or short spines at the unction of the
frustules, which are united into a filament. Valve surface either
simple punctate or punctate and areolate; punctate usually in
radiating lines or fascicules, often somewhat irregularly scattered
in the center. |
|
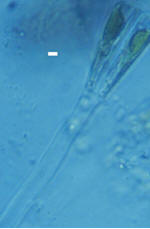 Gomphonema (Gomphonema
sp) Gomphonema (Gomphonema
sp)
Family Gomphonemateceae.
White
scale bar is 5 microns
Cells usually in
fan-shaped colonies, attached to dichotomously branched mucous
stripes, sometimes free. Valves symmetrical on the apical axis,
asymmetrical on the transapical axis. Valves naviculoid, more or
less elongated, clavate or cuneate. Apical nodules small, axial area
narrow, central area usually small, rounded. Raphe distinct,
straight. Valve surface striate, striae punctate, transverse or
slightly radiate. Girdle cuneate, simple. Connecting zone not
complex, broader in the upper end than the lower end. Valve with a
more or less distinct eccentric single central puncta. |
|
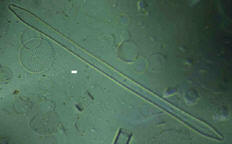 Synedra(Synedra sp.) Synedra(Synedra sp.)
Family Fragillariaceae.
White scale bar is 5 microns
Cells free or
united into ribbon-like or gan-like clustered star-like colonies.
Frustules linear, linear-lanceolate to very narrow lanceolate;
apical axis is occupied by the pseudoraphe.Valves surface usually
with transpical rows of deliate puncta and narrower pseudoraphe or
wide lanceolate, hyaline area sometimes with scattered
puncta.Lateral longitudinal ribs may be present in some forms. |
|
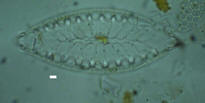 Surirella (Surirella sp.) Surirella (Surirella sp.)
Family Surirellaceae.
White scale bar is 5 microns
Cells solitary,
frustules in girdle view cuneate. Valves ovate, cuneate, reniform,
elliptical or linear. Asymmetrical on the trans-apical axis, upper
end usually broadly rounded, lower end cuneate or sub-acute. Valve
surface costate, costae either short, or lengthened so that they
meet at a median line in the apical axis. Central space often called
the pseudoraphe, linear, lanceolate, often obscure, sometime hyaline
or bearing faint folds or striae. Generally a bottom and littoral
form, occasionally occurring as plankton. |
|
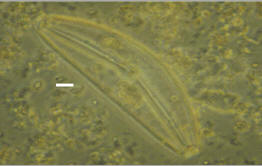 Cymbella (Calidris mauri) Cymbella (Calidris mauri)
Family Cymbellaceae.
White scale bar is 5 microns
Valve
asymmetrical to the apical axis. Dorsal margin convex, ventral
margin more or less straight; convex or concave. Axial area nearer
the ventral margin in most species; central area with or without
punctae. |
|
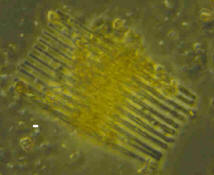 Tabellaria (Tabellaria sp.) Tabellaria (Tabellaria sp.)
Family Tabellariaceae.
White scale bar is 5 microns
Cells
quandrangular forming zigzag or straight filaments. Valves linear or
oblong, inflated in the middle and at the apices. Rectangular in
girdleview. Intercalary bands and septa present. In girdle view, the
septa appear as short thickened lines. In valve view the septa
extend at varying lengths under the surface of the valves. Valve
finely striated, striae transverse, costae absent. Pseduoraphe
narrow. |
|