BACKGROUND:
A common mistake made by manufacturers of dinosaur toys
and games is to call dinosaurs "prehistoric" animals. Strictly
speaking, the term "prehistoric" means before written history. Dinosaurs
certainly lived before humans or writing, but in practice prehistoric is
used by most people to refer to the time from the beginning of the Ice Age
(the Pleistocene Epoch, beginning 1.8 million years ago) to the beginning of
written history. Classifying dinosaurs as prehistoric leads to incorrect
notions, for example, that the dinosaurs were contemporaneous with large
mammals like mammoths and 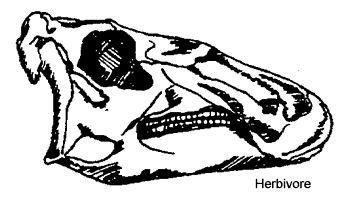 saber-toothed cats, or worse, that dinosaurs lived
at the same time as humans. saber-toothed cats, or worse, that dinosaurs lived
at the same time as humans.
The second goal of the Pre lab is to introduce the
concept of eating habits and food types. Different dinosaurs ate different
types of food. The Mesozoic dinosaurs included carnivores (meat-eaters),
herbivores (plant-eaters) and omnivores (plant- and meat-eaters).
Paleontologists can tell what different dinosaurs ate by looking at the
shape of their teeth and the shape of their bodies and comparing them with
the shapes of modern carnivores, herbivores and omnivores. Teeth are the
most common type of vertebrate body part found as fossils because they are
denser and more resistant to chemical destruction than the other bones in
the vertebrate 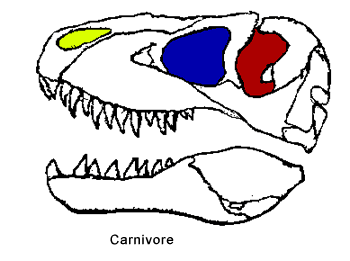 skeleton. From fossil teeth we get valuable information
about the eating habits, sizes, and growth patterns of ancient animals,
including dinosaurs. skeleton. From fossil teeth we get valuable information
about the eating habits, sizes, and growth patterns of ancient animals,
including dinosaurs.
Children (and even adults) often identify meat-eating
behavior as a negative trait and plant-eating behavior as a positive trait.
This mind-set leads to the bizarre notion of ‘good’ animals and ‘bad’
animals, especially when it comes to dinosaurs. We encourage you to address
this issue during the Pre Lab. Explain feeding habits in the context of the
food chain.
PROCEDURE:
- Before lab, mix the extinct dinosaurs, non-dinosaurs and prehistoric
animal models. Make enough collections for each student group.
- Discuss the difference between extinct and prehistoric animals with
the class. Point out that prehistoric (or Ice Age) animals lived with
our human ancestors and that some prehistoric animals are extinct (like
mammoths) and some are not (like bison). The dinosaurs lived long before
humans appeared on earth. Therefore, they are extinct but not
prehistoric.
- Have the students sort the animal model collections into dinosaurs,
non-dinosaurs and prehistoric animals.
The following are dinosaurs: Palaeocincus, Camptosaurus,
Brontosaurus (=Apatosaur), Iguanodon, Corythosaurus,
Tyrannosaurus, Brachiosaurus, Parasaurolophus, Ankylosaurus, Polacanthus,
Triceratops, Protoceratops, and Stegosaurus.
- Have the students color the worksheet.
|