BACKGROUND:
Human growth in body height usually stops at around
18-20 years. However, there are other portions of a human body that
will continue to grow like hair, fingernails, and fat cells. Adult
humans can get fatter, but rarely do they get taller. This lab focuses
on the hair and how it grows.
Hair is a threadlike structure that is used for insulation against
the cold. Mammal hairs are threadlike outgrowths of the skin.
Although the general structure of all human hair is similar, there
are some variations among ethnic groups. In fact, differences can
occur even among hair of people from the same regions. Human hair
is usually soft after birth and after a few months of infancy is
shed and replaced by the typical coarser hair which is longer and heavily
pigmented. Virtually the entire human skin is covered with hair,
though much of it is too fine to be visible. Hair is very sensitive
to the touch. The part above the skin is the shaft, below the skin
is the root.
PROCEDURE:
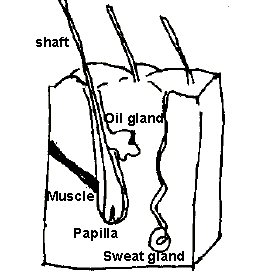 Draw the following picture of the
hair follicle on
the board and discuss the following parts with your students.
Draw the following picture of the
hair follicle on
the board and discuss the following parts with your students.
- muscle can move the hair shaft
- the papilla is the soft base of the shaft
- nerves help to interpret touch
- sweat glands extract salts, water, and acids from the
body
- oil glands keep skin soft, emit oil, prevent evaporation and
heat loss.
- Students will look at different types of hair during
lab. Hair is a part of the skin, which is the largest organ of the
human body. If you haven't purchased the module you can make baggies
of children's hair and save them. You may want to ask children weeks
before the lab that if they are getting a hair cut to save their hair in
a baggy and bring it to school.
- Use the recommended book as
a reference. The book shows the difference between the different
hair follicles. Straight hair has follicles that are round (in cross
section); wavy hair has follicles that are oval (in cross section); tight, curly hair has follicles that are flat (in cross section).