BACKGROUND:
A graph is a pictorial
presentation of a relationship among 2 or more items. Graphs can
be used to easily visualize a mathematical relationship. Define the
axis of a graph. Point out the vertical (y axis) and horizontal (x
axis) components. In graphing, the x is considered the independent
variable, whereas the y is the dependant variable (y is dependant on x).
In a common example, y represents the number of people and x represents
the year in whi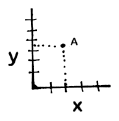 ch the number was counted. ch the number was counted.
Students usually see graphs
that are part of a rectangular Cartesian coordinate system. This
system is two dimensional. The term "Cartesian" is derived from the
French mathematician and philosopher Descartes (1596-1650) who was noted
for his logical analysis and mechanical interpretation of the physical
world. Cartesian coordinates help locate a point by using a reading
from the x axis and one from the y axis. For instance, in the graph
to the right, point A is located by finding its x and y axis.
PROCEDURE:
- The student
constructed a bar graph in lab. In this activity, students look at
a line graph and ask themselves questions about the graph to extrapolate
an answer. Extrapolate means that students will predict or extend
how the graph will continue. The points on the graph can be read
from the x and y axis.
- The worksheet revolves
around the population of California. If located in another state,
make this graph more representative of your area. California is now
the most populous state in the United States, with about 28 million people.
New York was the most populous state up until 1989. According to
this graph, it looks as if California will be the leader for a long time
to come.
- Students are learning
to extrapolate the future by using past data. This is a common practice
in determining future trends.
- ANSWERS:
2. increased, 3. 19 million, 4. double, 5. run
out of space to live, shortage of housing, not enough food, increased use
of natural resources (timber, water, oil, etc) and (5) pollution increase
|