BACKGROUND:
Electromagnetic waves
are all around us and range from common light to radio waves and gamma
rays. These waves are related to electricity and magnetism in that both
sources produce these waves. All substances have a positive and negative
side, no matter how big or small they are. Two positives or negatives
repel each other, while positives and negatives attract each other.
Atomic particles are constantly being hit and deflected. As the world is
made up of negatives and positives, energy is constantly being
generated. It is like a "bumper car" game. Electromagnetic
waves are the consequence of all this bumping. It is difficult to
understand this concept, but students need to become familiar with the
terms to facilitate their understanding at a later time.
 These waves act like
the waves we have already seen. Unfortunately, we cannot see the wave
motions with our eyes. When an electromagnetic charge is suddenly
displaced, a ripple of electric and magnetic force is generated in the
same manner in which water ripples are formed by dropping a pebble.
Electromagnetic waves, unlike sound (physical) waves can move through a
vacuum for they do not require a medium for their existence. They are
waves of force. These waves act like
the waves we have already seen. Unfortunately, we cannot see the wave
motions with our eyes. When an electromagnetic charge is suddenly
displaced, a ripple of electric and magnetic force is generated in the
same manner in which water ripples are formed by dropping a pebble.
Electromagnetic waves, unlike sound (physical) waves can move through a
vacuum for they do not require a medium for their existence. They are
waves of force.
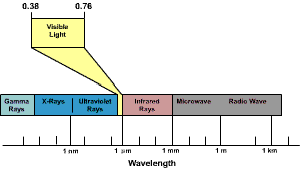
This activity tries
to show the variety of waves that are included in electromagnetic waves.
Familiarize students with the terms. Many of your students know about
these waves, they just don't connect how they are related.
Radio waves'
wavelength are the longest wavelength. On a radio, the channels refer to
the frequency. There are two common ways to transmit radio, AM
(amplitude modulation) and FM (frequency modulation). Modulation refers
to how the wave is varied through its transmission. AM varies its
amplitude (strength), while FM varies its frequency.
Television waves have
shorter wavelengths than most radio waves. Television is transmitted
from distant stations. The television at home picks up these waves and
interprets them for us to see. There are UHF and VHF components of
television waves.
Microwaves have a higher frequency
and as their name suggests, have smaller wavelengths. Microwaves are
used not only to cook but also in the communication industry.
Infrared waves are even smaller and are known for their use in detecting
heat. A cat's eye can detect infrared light that is why they say a cat
sees in the dark. Their eyes detect what human eyes cannot.
Visible light is the
spectrum that we are most familiar with. Visible light can be broken
into the colors of the rainbow, because each of the colors has a
different wavelength and frequency.
Ultraviolet light is
known to be harmful to human skin. It is the ozone layer that helps
protect us from these rays. However, ultraviolet light can also help
kill harmful bacteria.
X-rays are known for
their use in viewing inside our body. X-rays can go through soft matter
and can outline hard matter. The many uses for X-rays are still not
completely known.
Gamma rays and cosmic
rays are at the extreme right of the spectrum. Scientists are still
trying to unravel their mysterious powers. The rays seem to be very
powerful when concentrated, but only the future knows how they will be
useful in our society. PROCEDURE:
Instruct students to use the
worksheet to discover the parts of the electromagnetic wave spectrum.
ANSWERS:
1. gamma and cosmic rays.
2. Television and radio waves.
3. Visible light.
4. Sound wave, it is not an electromagnetic wave but a physical wave.
5. Microwave ovens, communications.
6. Broadcasting
station
7. Broadcasting station
|